Edge Services (GCP)
This guide helps you deploy Edge Services (e.g., Redact or AI Guard) in a GCP environment, either as a standalone container on Google Cloud Run or as part of a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. Choose the deployment method that best fits your needs: Cloud Run for simplicity or GKE for scalable production workloads.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following before starting the deployment:
- A GCP account with sufficient IAM permissions to manage Cloud Run or GKE resources
- gcloud CLI installed and authenticated with your account
- Docker installed and configured (optional)
- Access to Pangea's private Docker Hub repository (granted by a Pangea representative)
- Set up Vault/Edge services to get below environment variables
Environment configuration
Select a service from the buttons below to configure your Edge Deployment.
AI Guard
Redact
Environment variables
Use values from your Pangea Console to set these environment variables.
PANGEA_CSP=aws # Cloud Service Provider
PANGEA_VAULT_TOKEN=pts_XXX # Vault Token
PANGEA_REGION=us # Deployment Region
PANGEA_AI_GUARD_TOKEN=XXX # Service Token for AI Guard
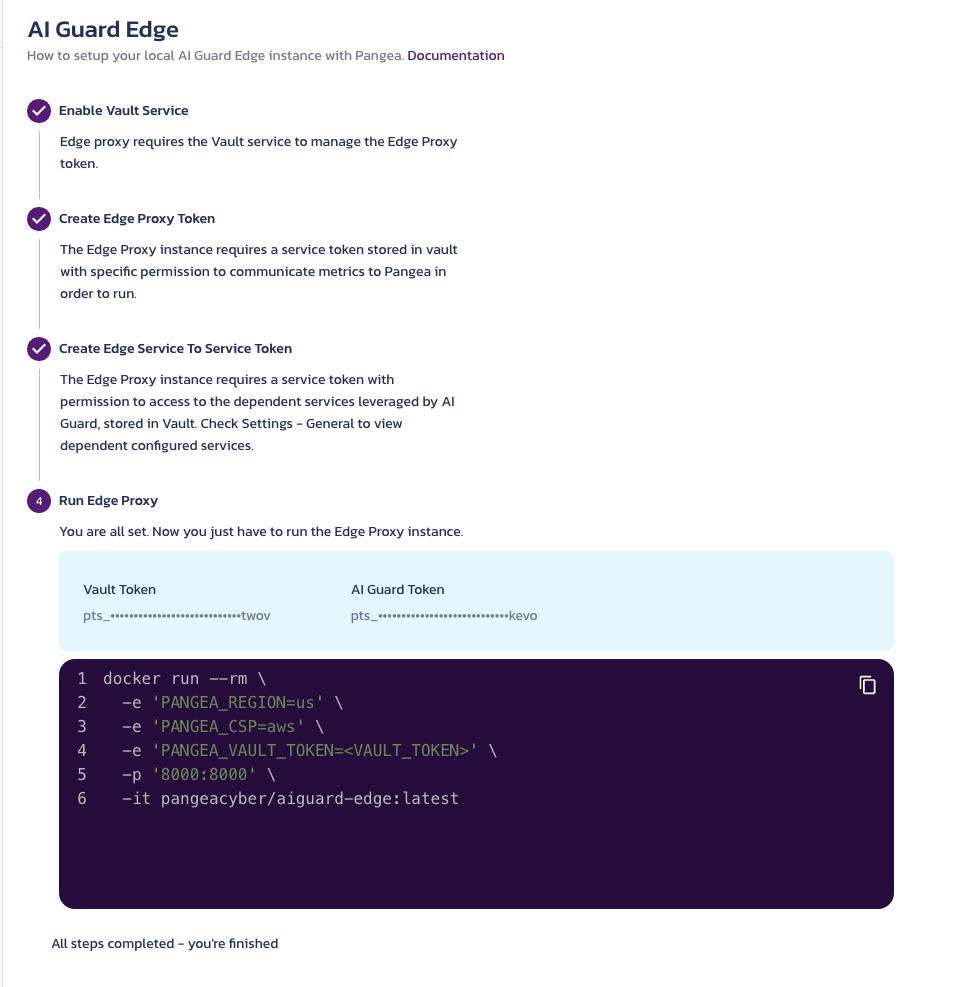
These variables can be found in your Pangea Console under the Edge Configuration section:
- Navigate to your Pangea Console
- Go to "Services" >> Select your service (e.g., "Redact" or "AI Guard") >> and under Settings, you will find "Edge"
- After you complete the preliminary steps for this, you should find the following page:
Copy these directly from the console so you can set these variables in your environment using:
export PANGEA_CSP=aws
export PANGEA_VAULT_TOKEN=pts_XXX
# ... repeat for other variables
Keep these tokens secure and never commit them to version control.
Docker registry access
Pull the Edge Service container image from Pangea's private repository.
docker pull pangeacyber/aiguard-edge:latest
You will need to be granted access via Pangea to follow this step. This will be a good preliminary step to ensure your environment is set up to follow the rest of the guide.
Cloud Run deployment
For simpler workloads, deploy Edge Services using Google Cloud Run.
-
Enable Cloud Run API Ensure that the Cloud Run API is enabled in your project:
gcloud services enable run.googleapis.com -
Build and push the image If required, tag the image and push it to Google Container Registry (GCR):
docker tag pangeacyber/ai-guard:latest gcr.io/<your-project-id>/ai-guard:latest
docker push gcr.io/<your-project-id>/ai-guard:latest -
Deploy to Cloud Run Deploy the container to Cloud Run:
gcloud run deploy ai-guard-edge \
--image=gcr.io/<your-project-id>/ai-guard:latest \
--region=us-central1 \
--platform=managed \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--memory=2Gi \
--port=8000 \
--set-env-vars "PANGEA_REGION=us,PANGEA_CSP=aws,PANGEA_VAULT_TOKEN=<your-vault-token>" -
Get the service URL After deploying, use this command to retrieve the URL of the deployed Cloud Run service:
gcloud run services describe ai-guard-edge --region=us-central1 --format="value(status.url)"The output will provide the full URL of the service, which you can use for testing.
-
Test the service Replace
<service-url>in the test command with the URL obtained from the previous step:curl -sSLX POST 'https://<service-url>/v1beta/text/guard' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <your-ai-guard-token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"text": "This is test text with sensitive data SSN: 234-56-7890"}'
GKE deployment
For production environments, deploy Edge Services on GKE to take advantage of container orchestration, scaling, and high availability features.
-
Create a GKE cluster
If you don’t have a GKE cluster, follow the GKE Quickstart Guide to create one.
noteSome requirements for the cluster:
- Ensure an AMD64 node pool is available unless ARM64 compatibility is required.
- Configure the VPC and networking settings appropriate for your environment.
- For this deployment, use an nginx ingress controller to expose services externally.
-
Configure access to your cluster
Use the
gcloudCLI to configurekubectlaccess and create a namespace:gcloud container clusters get-credentials <cluster-name> --zone <zone> --project <project-id>
kubectl create namespace pangea-edge -
Create a Docker pull secret
To pull the Edge Service image from Pangea's private repository, create a file named
pangea_dockerhub_pull_secret.yaml:apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: pangea-registry-key
namespace: pangea-edge
type: kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
data:
.dockerconfigjson: [base64-encoded-docker-config]noteReplace
[base64-encoded-docker-config]with the base64-encoded Docker credentials. More details can be found here. -
Apply the Docker pull secret
Save and apply the secret to the namespace:
kubectl apply -f pangea_dockerhub_pull_secret.yaml -
Create a Vault token secret
Create a secret for the Vault token in a file named
pangea_vault_token.yaml:apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: vault-token
namespace: pangea-edge
type: Opaque
data:
PANGEA_VAULT_TOKEN: [base64-encoded-vault-token]noteReplace
[base64-encoded-vault-token]with the base64-encoded Vault token obtained from the environment configuration. -
Apply the Vault token secret
Save and apply the secret to the namespace:
kubectl apply -f pangea_vault_token.yaml -
Deploy Edge service
Create a deployment configuration file named
pangea_ai_guard_deployment.yaml.apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
namespace: pangea-edge
name: ai-guard-edge
labels:
app: ai-guard-edge
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ai-guard-edge
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ai-guard-edge
spec:
containers:
- name: ai-guard-edge
image: pangeacyber/ai-guard:latest
env:
- name: PANGEA_REGION
value: "us"
- name: PANGEA_CSP
value: "aws"
- name: PANGEA_VAULT_TOKEN
value: "/var/run/secrets/PANGEA_VAULT_TOKEN"
- name: AI_GUARD_CONFIG_DATA_COMMON_CLOUD_ONPREM_BM_RECORD_LOCAL_SUBMISSION_ENABLED
value: "true"
volumeMounts:
- name: ephemeral-storage
mountPath: "/var/pangea/data"
- name: pangea-vault-token
mountPath: /var/run/secrets
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
cpu: 500m # 500 millicores (0.5 CPU)
memory: 4Gi # 4 GiB of memory
volumes:
- name: ephemeral-storage
emptyDir: {}
- name: pangea-vault-token
secret:
secretName: vault-token
imagePullSecrets:
- name: pangea-registry-keyApply the deployment:
kubectl apply -f pangea_ai_guard_deployment.yaml -
Expose the deployment
Create a service file named
pangea_ai_guard_service.yamlto expose the deployment:apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
namespace: pangea-edge
name: ai-guard-edge-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: ai-guard-edge
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000Apply the service configuration:
kubectl apply -f pangea_ai_guard_service.yaml -
Set up ingress
Create an ingress configuration file named
simple-edge-ingress.yaml:apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ai-guard-edge-ingress
namespace: pangea-edge
spec:
ingressClassName: gce
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: ai-guard-edge-service
port:
number: 8000Apply the ingress configuration:
kubectl apply -f simple-edge-ingress.yaml -
Test the deployment
Use the external IP address from the load balancer to test. You can get the external IP by running this command:
kubectl get service ai-guard-edge-service -n pangea-edgeThen test the API using:
curl -sSLX POST 'http://<external-ip>:8000/v1beta/text/guard' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <your-ai-guard-token>' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"text": "This is test text with sensitive data SSN: 234-56-7890"}'
Monitoring and troubleshooting
Use the gcloud CLI or kubectl to debug:
# View logs for Cloud Run
gcloud logging read "resource.labels.service_name=redact-edge" --limit=100
# View pod logs for GKE
kubectl logs -n pangea-edge -l app=redact-edge
# Check pod status for GKE
kubectl get pods -n pangea-edge
If you're not receiving a response, it's often due to a pod restart. You can use the above commands to check the pod logs.
Was this article helpful?