Private Cloud Prerequisites
Access to Pangea's private OCI registry
-
Sign up for a free
Pangea account . -
After creating your account and first project, skip the wizards. This will take you to the Pangea User Console, where you can enable the access.
-
In your Pangea User Console , under Home, click Private Cloud in the navigation sidebar.
-
If access to Private Cloud resources is not yet enabled for your organization, click Request Access.
-
Once access is granted, refresh the Private Cloud page and complete all steps using the clickable buttons:
-
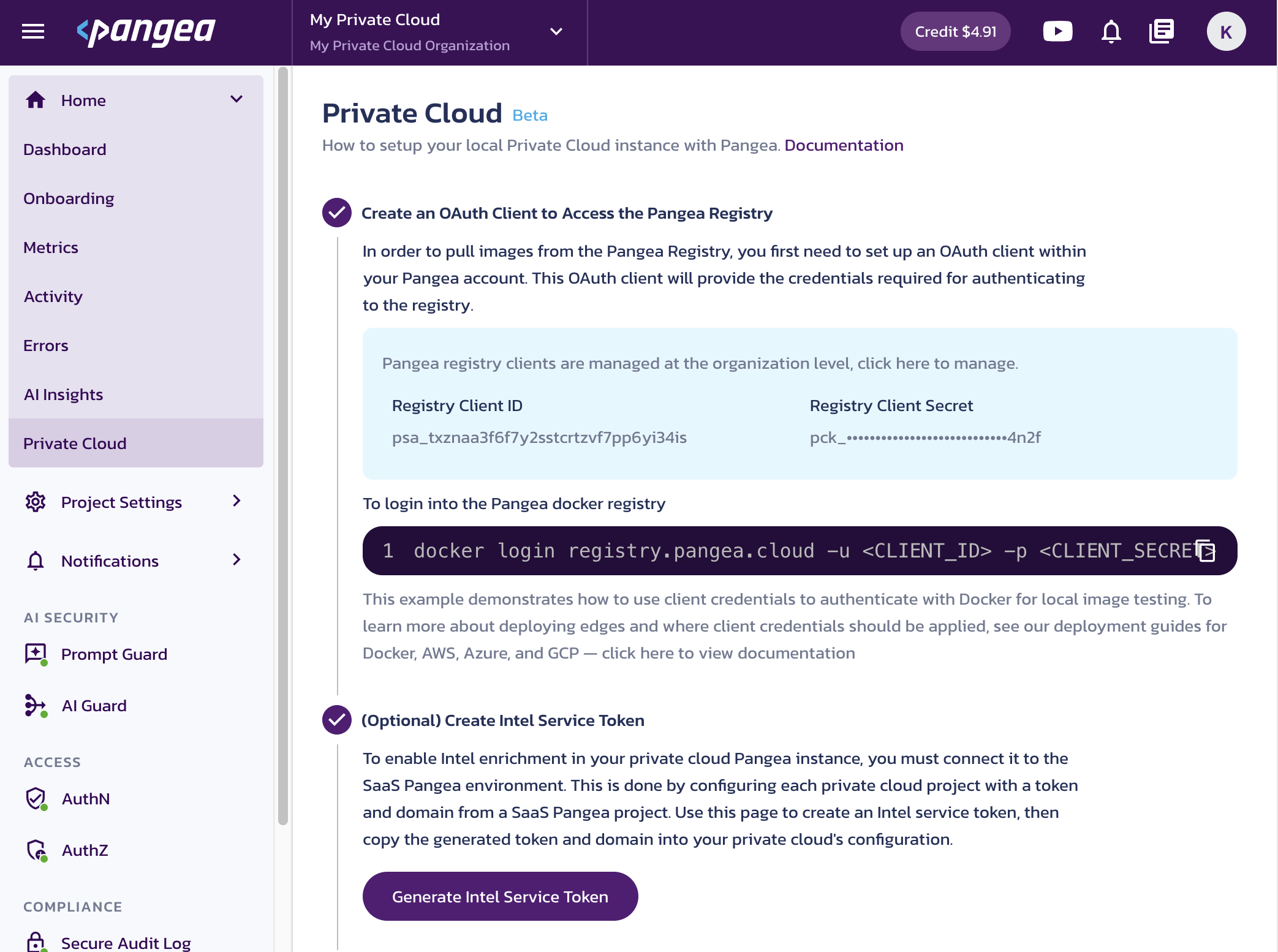
Create an OAuth Client to Access the Pangea Registry
Click Create Registry Client, then capture the credentials for accessing the private OCI registry:
- Registry Client ID - Used as the username to access the Pangea registry.
- Registry Client Secret - Used as the password to access the Pangea registry.
Click a value to copy it to the clipboard.
tip:You can manage your Private Cloud and other organizational clients on the Organization API Credentials page. Click Organization Settings from the menu that opens when you click your profile icon in the Pangea User Console to access it.
To test access to the Pangea Registry, run the example command in your terminal.
Example login commandhelm registry login registry.pangea.cloud \
--username <CLIENT_ID> \
--password-stdin <<< <CLIENT_SECRET> -
(Optional) Create Intel Service Token
Intel enrichment relies on SaaS-hosted threat intelligence. To enable it in your Private Cloud deployment, each project must be linked to a SaaS Pangea project using a token and domain.
Click the button to generate Intel service token, then copy both the token and domain into your Private Cloud project configuration.
-
Cloud service provider account
You will need tools and permissions to create and manage cloud resources, networking, and storage:
- Kubernetes cluster such as EKS, AKS, or GKE
- PostgreSQL instance for storing Pangea service data
- Extensions:
pgvector- Required by Prompt Guard, the service that powers malicious prompt protection in AI Guard You must install this extension, which stores customer-provided data used to improve LLM detectionspgmq- Used by multiple Pangea services for internal queueing. No action is required; this extension is installed automatically if not already present.
- Storage:
- A Kubernetes
StorageClassthat supports theReadWriteOnce(RWO) access mode, required by the persistent volume for the database
- A Kubernetes
- Extensions:
- Ingress controller for routing external traffic to services and UI, and a TLS certificate for secure access
- Some services require additional resources:
- File storage, such as AWS S3 - Required for the Secure Audit Log service
Tools installed locally
kubectlinstalled and configured to access the clusterhelminstalled (version 3 or higher)
Environment-specific adjustments
Some steps - such as storage-class definitions, network policies, and DNS or ingress setup - may vary depending on your Kubernetes distribution or organizational requirements. Adapt the commands in these guides to fit your environment as needed.
Was this article helpful?