Getting Started
Review the steps to integrate File Scan into your app
Introduction
The File Scan service must be enabled from the
Pangea Console before use. Make sure you have access to the Pangea Console and that you've created a project.To create a project or learn about projects, visit Creating a project.
Create a token
Expand for details
Create a token so that you can access the File Scan endpoints:
- Go to the Pangea Console and click File Scan in the left-hand navigation menu. The File Scan Overview page will appear.
- On the File Scan Overview page, you'll see a notification asking you to set a service token. Click Create new token toward the bottom right side of your screen.
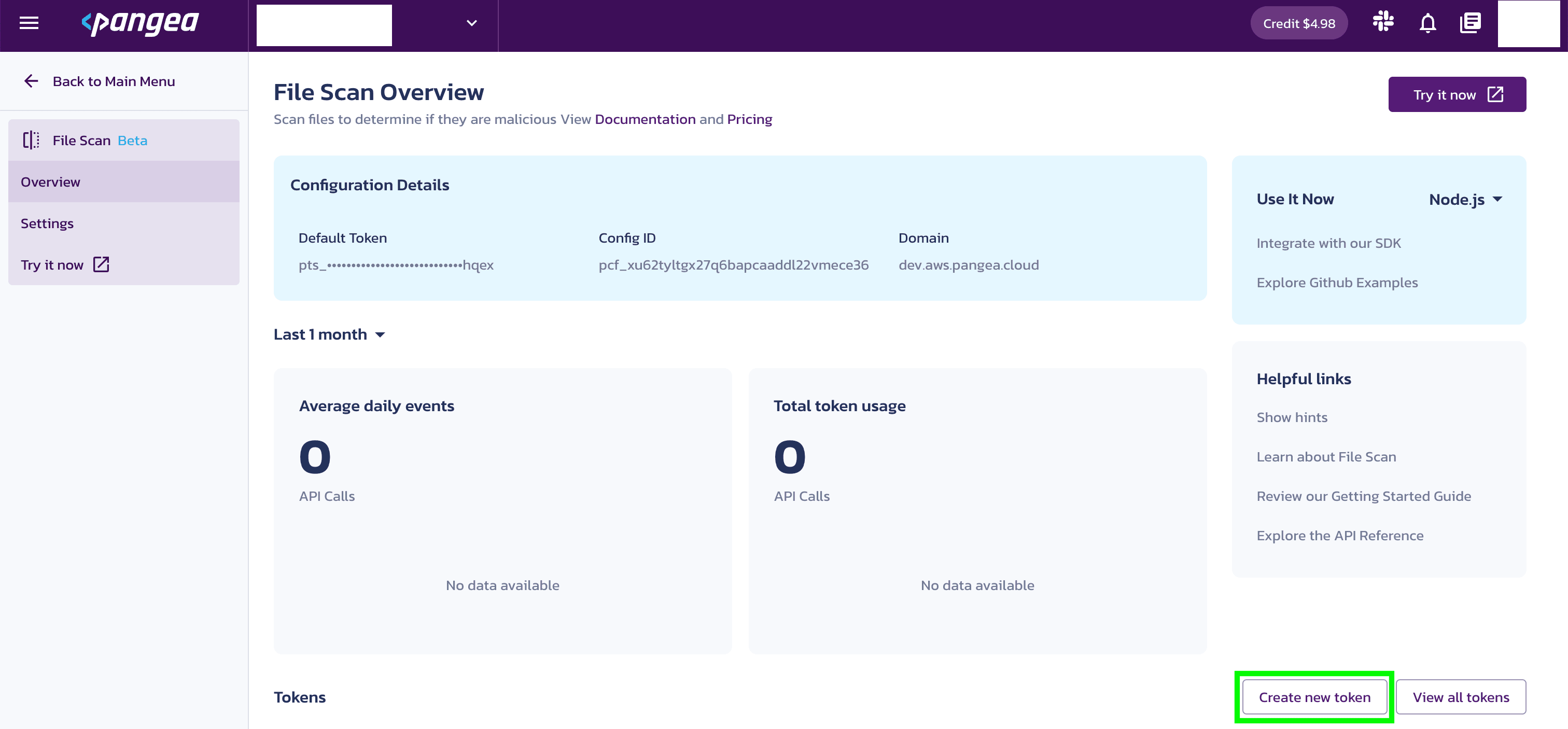
- You’ll be prompted to create a token. Enter a Token name and select an Expiration Date. You may also create a token for all Intel services, if you wish.
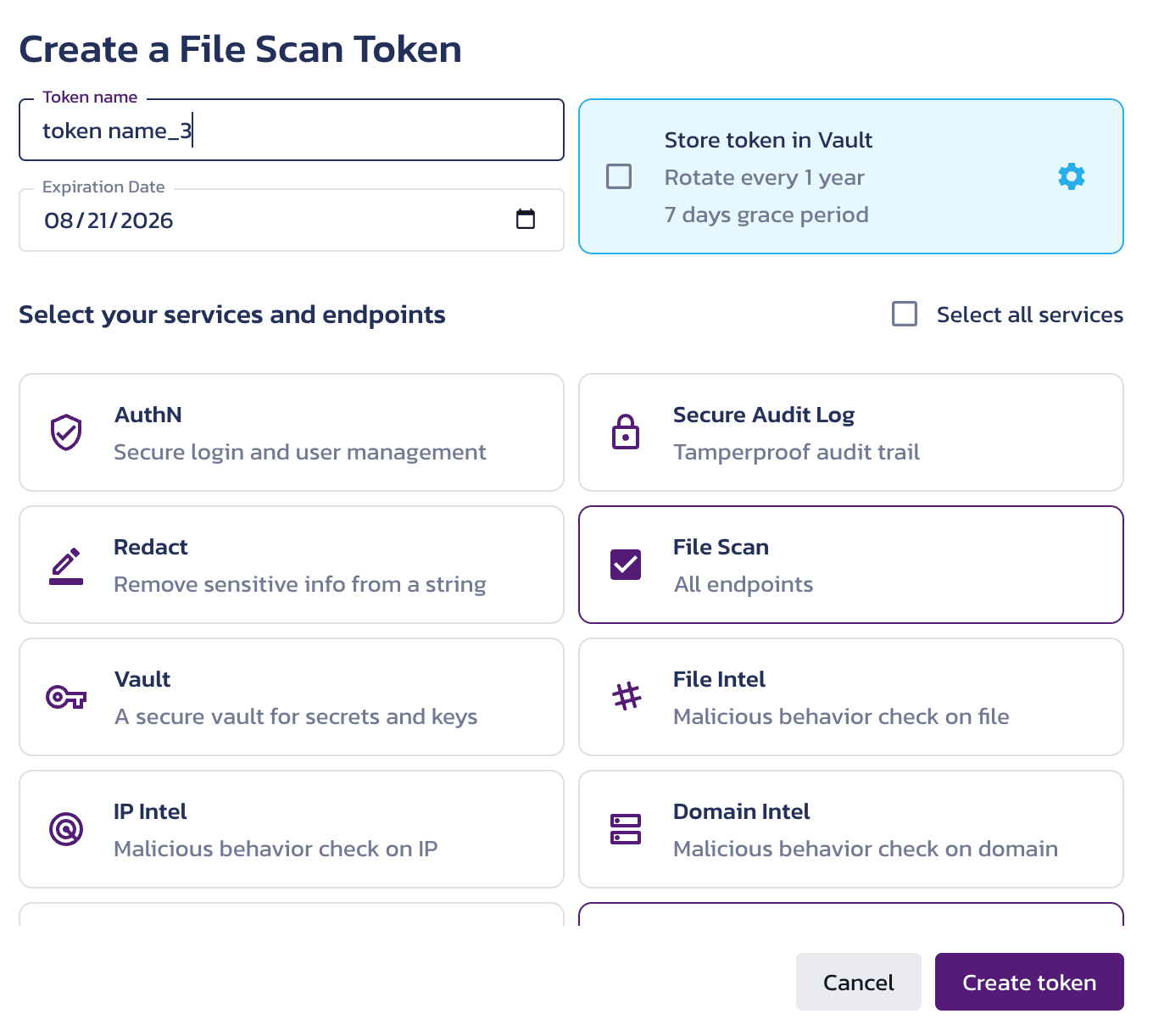
- Once configured, the token is available in the Tokens section of the File Scan Overview page.
Select your provider
Expand for details
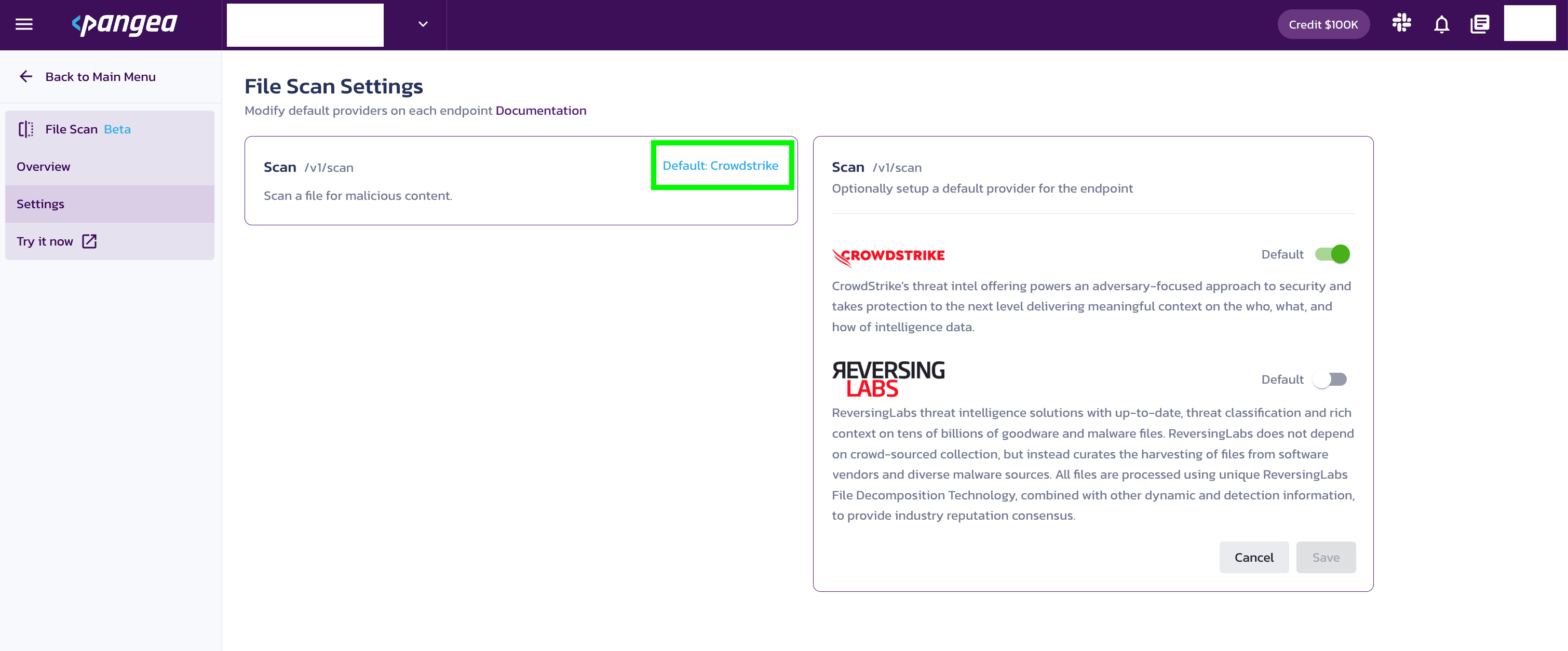
Default providers can be selected in the Pangea Console . Setting a default provider in the Pangea Console means your API request calls will use this provider, unless another provider is specified as part of your API request.
To select a default provider for an API:
- Go to the Pangea Console .
- On the left-hand navigation menu, select File Scan.
- On the left-hand navigation menu, select Settings.
- On the right-hand side, select the default provider.
Test the service
The interactive File Scan API Reference allows you to test API endpoints from the documentation. This is an easy way to play around with the /v1/scan endpoint to submit a file, get the response, and see File Scan results.
Configure your app for communication with the Pangea service
For your app to communicate with the Pangea service, you will need to know the token and domain from the File Scan Configuration Details.
The examples in this documentation use the PANGEA_DOMAIN and PANGEA_FILE_SCAN_TOKEN environment variables for this purpose.
The token and domain Configuration Details are created when you enable File Scan and can be found in the Overview section under File Scan.
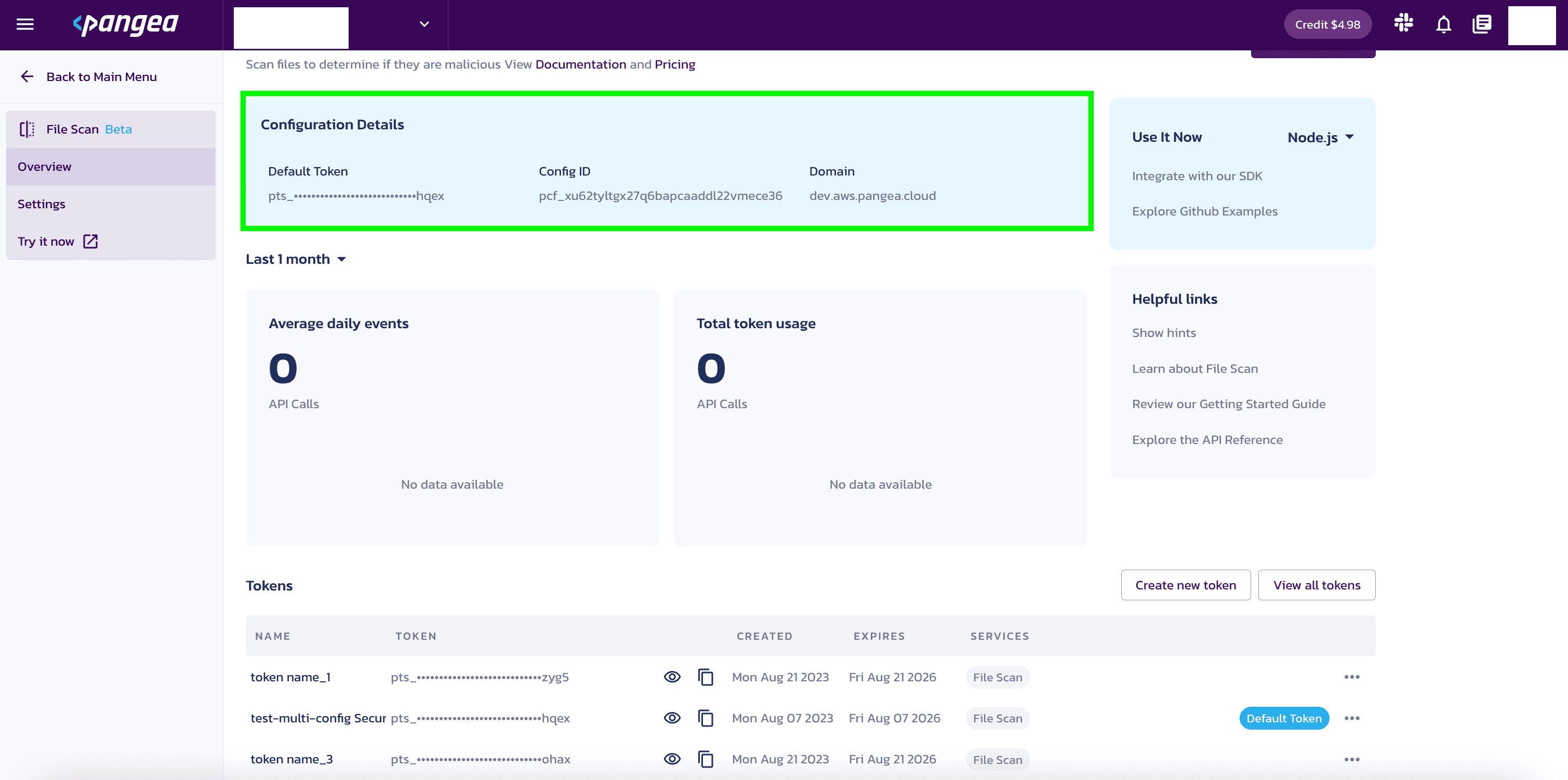
Set environment variables
Set the PANGEA_DOMAIN and PANGEA_FILE_SCAN_TOKEN environment variables containing the token and domain information so that copied and pasted documentation examples will work for you.
In the examples below, replace "yourServiceDomain" with domain and "yourAccessToken" with token from your Configuration Details.
export PANGEA_DOMAIN="yourServiceDomain"
export PANGEA_FILE_SCAN_TOKEN="yourAccessToken"
curl -sSLX POST 'https://file-scan.'"$PANGEA_DOMAIN"'/v1/scan' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer '"$PANGEA_FILE_SCAN_TOKEN" \
-H 'Content-Type: multipart/form-data' \
-F 'request={"provider":"crowdstrike"};type=application/json' \
-F 'upload=@path-to-my-file.ext;type=application/octet-stream'
The File Scan API is generally asynchronous. A successful call will normally return an HTTP 202 status code and response that includes a request_id. When CrowdStrike is the provider, the File Scan API can return an HTTP 200 status code when the verdict is determined by a reputation lookup.
In the example below, the returned request_id is prq_j4xxpqqtbfmpgbydefct7xglytxe5xie:
{
"request_id": "prq_j4xxpqqtbfmpgbydefct7xglytxe5xie",
"request_time": "2023-09-21T03:13:07.995895Z",
"response_time": "2023-09-21T03:13:09.224183Z",
"status": "Accepted",
"summary": "Your request is in progress. Please check(GET https://file-scan.aws.us.pangea.cloud/request/prq_j4xxpqqtbfmpgbydefct7xglytxe5xie) for status of the request later.",
"result": {
"ttl_mins": 7200,
"retry_counter": 0,
"location": "https://file-scan.aws.us.pangea.cloud/request/prq_j4xxpqqtbfmpgbydefct7xglytxe5xie"
}
}
To fetch the final response, you must poll using a GET request with the request_id from the File Scan API call above until you get an HTTP 200 status code.
For example:
curl -sSLX GET 'https://file-scan..'"$PANGEA_DOMAIN"'/request/prq_j4xxpqqtbfmpgbydefct7xglytxe5xie' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer '"$PANGEA_FILE_SCAN_TOKEN" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
An example final response would be:
{
"request_id": "prq_j4xxpqqtbfmpgbydefct7xglytxe5xie",
"request_time": "2023-09-21T03:13:07.995895Z",
"response_time": "2023-09-21T03:13:57.435935Z",
"status": "Success",
"summary": "File was scanned",
"result": {
"data": {
"category": [
"win/malicious_confidence_100"
],
"score": 100,
"verdict": "malicious"
},
"raw_data": {
"reputation": {},
"scan": {
"ArchiveInfo": {
"clean_files": 0,
"dirty_files": 0,
"errors": 0,
"files_scanned": 0,
"potentially_unwanted_files": 0
},
"confidence": "high",
"detection_name": "win/malicious_confidence_100",
"prediction": "malicious"
}
}
}
}
For details, visit the SDK documentation. If you don't see the language you need,
let us know.And remember: The interactive File Scan API Reference allows you to test API endpoints from the documentation.
Understand the response
After the File Scan asynchronous request has finished processing, your application can fetch the outcomes and obtain a JSON response.
The normalized score and verdict are given in the data section of the response.
If raw=true is used, reputation or scan details (depending on which was used to reach a verdict and score) are available in the raw_data section.
Here is an example final response from a File Scan call with raw=true and provider=crowdstrike:
Sample JSON response to the POST method
{
"request_id": "prq_5pakppam2ntf53nlca3fu2ype6wngann",
"request_time": "2023-08-26T00:58:35.899904Z",
"response_time": "2023-08-26T00:58:39.326361Z",
"status": "Success",
"summary": "File was scanned",
"result": {
"data": {
"category": ["win/malicious_confidence_100"],
"score": 100,
"verdict": "malicious"
},
"raw_data": {
"reputation": {},
"scan": {
"ArchiveInfo": {
"clean_files": 0,
"dirty_files": 0,
"errors": 0,
"files_scanned": 0,
"potentially_unwanted_files": 0
},
"confidence": "high",
"detection_name": "win/malicious_confidence_100",
"prediction": "malicious"
}
}
}
}
Here is an example final response from a File Scan call with raw=true and provider=reversinglabs:
Sample JSON response to the GET method
{
"request_id": "prq_ilfzr42s5i7lb626fsdtij5jtlojgmp3",
"request_time": "2023-09-21T03:48:00.748586Z",
"response_time": "2023-09-21T03:48:44.073002Z",
"status": "Success",
"summary": "File was scanned",
"result": {
"data": {
"category": ["ByteCode-MSIL.Trojan.RedLine"],
"score": 100,
"verdict": "malicious"
},
"raw_data": {
"info": {
"statistics": {
"file_stats": [
{
"type": "Image",
"subtype": "None",
"count": 6,
"identifications": [
{
"count": 6,
"name": "PNG:Generic"
}
]
},
{
"type": "Text",
"subtype": "XML",
"count": 1,
"identifications": [
{
"count": 1,
"name": "Unknown"
}
]
},
{
"type": "PE",
"subtype": ".Net Exe",
"count": 1,
"identifications": [
{
"count": 1,
"name": "Unknown"
}
]
}
]
},
"file": {
"file_type": "PE",
"file_subtype": ".Net Exe",
"size": 1453056,
"entropy": 7.931315612603161,
"hashes": [
{
"name": "imphash",
"value": "f34d5f2d4577ed6d9ceec516c1f5a744"
},
{
"name": "md5",
"value": "5be56d52f7563020f5ebd9c605031d8b"
},
{
"name": "rha0",
"value": "547bb74558c8fe53c59bd52994a0bddb88c84edf"
},
{
"name": "sha1",
"value": "4faec9ad61c7a40aac0f7182dc8d97ff8ba66a7d"
},
{
"name": "sha256",
"value": "81cc8e439194bb4349d76b87933684c288b855e4ff07d16263ff28c034ad0fc6"
}
]
},
"identification": {
"success": false,
"name": "",
"version": "",
"author": ""
}
},
"classification": {
"propagated": false,
"classification": 3,
"factor": 5,
"result": "ByteCode-MSIL.Trojan.RedLine",
"scan_results": [
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 3,
"factor": 5,
"name": "Antivirus (based on the RCA Classify)",
"version": "2.84",
"result": "ByteCode-MSIL.Trojan.RedLine",
"rca_factor": 10,
"properties": [
{
"name": "scannerCount",
"value": "19"
},
{
"name": "scannerMatch",
"value": "15"
},
{
"name": "vendorCount",
"value": "19"
},
{
"name": "vendorMatch",
"value": "15"
},
{
"name": "firstSeen",
"value": "2022-12-25T11:51:00"
},
{
"name": "lastSeen",
"value": "2023-09-05T05:14:08"
}
]
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "internal",
"classification": 3,
"factor": 1,
"name": "TitaniumCore Machine Learning",
"version": "4.1.2.0",
"result": "ByteCode-MSIL.Malware.Heuristic",
"rca_factor": 6
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "k7computing",
"result": "Trojan (0059cd511)",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "ahnlab_online",
"result": "Trojan/Win.Injection.C5354857",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "antivir",
"result": "detected",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "avast",
"result": "Win32:CrypterX-gen [Trj]",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "bitdefender",
"result": "Gen:Variant.MSILHeracles.57143",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "carbonblack",
"result": "trojan",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "clamav",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "crowdstrike",
"result": "win/malicious_confidence_80",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "crowdstrike_online",
"result": "malicious confidence 100%",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "drweb",
"result": "Trojan.Inject4.49886",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "fireeye_online",
"result": "Generic.mg.5be56d52f7563020",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "fortinet",
"result": "MSIL/Kryptik.AHKP!tr",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "mcafee_online",
"result": "GenericRXVF-QU!5BE56D52F756 (trojan)",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "microsoft_online",
"result": "Trojan:MSIL/Redline.GDA!MTB",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "panda_online",
"result": "Trj/Chgt.AA",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "quickheal",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "rising_online",
"result": "Malware.Obfus/MSIL@AI.100",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "sentinelone_online",
"result": "DFI - Malicious PE",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "sophos_susi",
"result": "Mal/Generic-S",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "symantec_beta",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "trendmicro_consumer",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "vba32",
"result": "TScope.Trojan.MSIL",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "gdata",
"result": "Gen:Variant.MSILHeracles.57143",
"rca_factor": 0
},
{
"ignored": false,
"type": "av",
"classification": 0,
"factor": 0,
"name": "ikarus",
"result": "Trojan.MSIL.Crypt",
"rca_factor": 0
}
],
"rca_factor": 10
},
"story": [
{
"caption": "Description",
"content": "This file (SHA1: 4faec9ad61c7a40aac0f7182dc8d97ff8ba66a7d) is a 32-bit portable executable .NET application. The application uses the Windows graphical user interface (GUI) subsystem. According to version information, this is Swayercitrons.exe. Module name is Swayercitrons.exe with version ID FACB8921-E7E2-4C4A-BBD7-4372E6BC4AD6. It references assemblies Swayercitrons, System.Drawing and mscorlib, among others. This application has access to device configuration, monitoring and running processes and has cryptography and security related capabilities. There are 7 extracted files."
},
{
"caption": "Classification",
"content": "The application was classified as malicious, with the name ByteCode-MSIL.Trojan.RedLine, using antivirus detection. One other scanner confirms the classification."
}
]
}
}
}
Understand and review results
The API response sent by File Scan includes various fields and values; however, the ones listed below give you the most information about the disposition of a File Scan. To learn about more response fields, visit the File Scan API Reference.
verdict | The verdict normalized categorization as interpreted by the data returned by the third party provider. There are four possible verdicts:
|
score | The normalized score as interpreted by the data returned by the third party provider. Scores are associated with the verdict values listed above:
|
category | Indicates the category associated with the file. This field may return more than one category and may, at times, not be populated. |
raw_data | Raw data returned by the provider you specified in the API request. You
can investigate the raw data if its meaningful to your use case or if
you want to supply it to your users. You must set the |
To learn about the response fields above, visit the File Scan API Reference.
Was this article helpful?